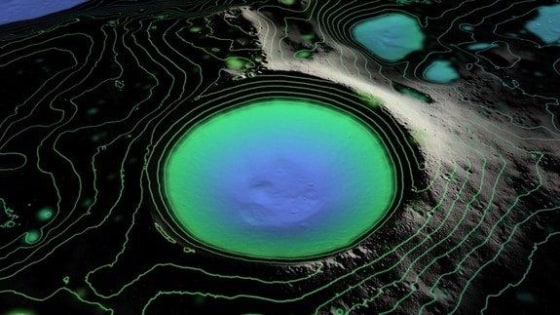
Some parts of the moon haven't seen the sun in millions, and even billions, of years but an unmanned NASA spacecraft is shedding light on these lunar lands of permanent darkness.
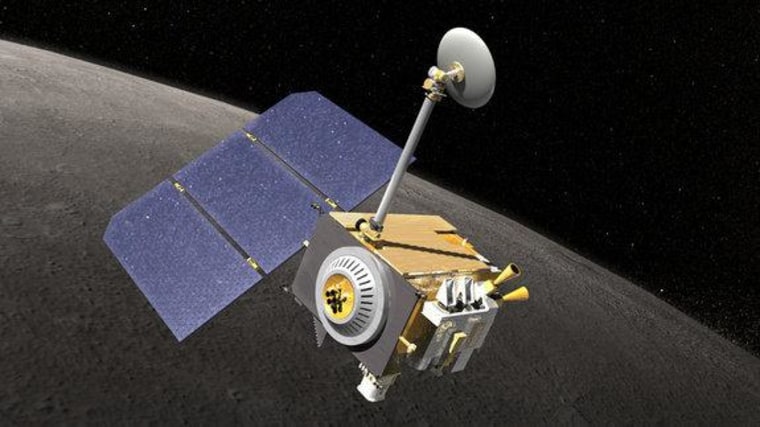
A new video from NASA's Goddard Space Flight Center Scientific Visualization Studio explains just how the agency's powerful Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO) is collecting data on the moon's coldest, darkest craters.

Earth's axis is titled about 23.4 degrees from vertical, meaning sunlight reaches every surface, even the north and south poles, for at least part of the year. The moon, meanwhile, is tilted just 1.6 degrees, nearly perpendicular to the direction of the sun's light. This means that there are some deep craters near the moon's poles that haven't seen the sun for over 2 billion years.
Scientists are interested in the moon's permanently shadowed regions because they are thought to have the right conditions to trap volatiles such as water, which would normally vaporize and escape into space, according to NASA. In fact, LRO helped confirm the presence of water ice on the moon along with other lunar probes from Japan and India. In October 2009, LRO detected the presence of frozen water when its sister craft, Lunar CRater Observation and Sensing Satellite, crashed into a permanently shadowed crater near the moon's south pole.
NASA launched the $504 million LRO mission in June 2009. The spacecraft is equipped with a suite of instruments, including a laser ranging tool, to create the most-detailed ever topographical maps of the lunar surface of its mysterious shadowed regions. The lunar probe also has tools designed to measure temperature and neutron absorption in the moon's darkest corners.
And while the sun can't get into the moon's permanently shadowed regions, LRO's Lyman Alpha Mapping Project (LAMP) instrument can detect how faint light from others stars reaches some of these craters.
Google+. Follow us @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com
- Dark Craters Of The Moon Get 'Lit Up' | Video
- 10 Surprising Moon Facts
- Moon Master: An Easy Quiz for Lunatics
- How to Observe the Moon (Infographic)
Copyright 2013 Space.com, a TechMediaNetwork company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.