By Nola Taylor Redd
Elements of a giant cyclone circling above the south pole of Venus constantly break apart and re-form, according to new research. Scientists studying observations of the planet taken over the last six years have concluded that the long-lived storm is constantly evolving, raising even more questions about the unusual weather formation.
A storm on the move
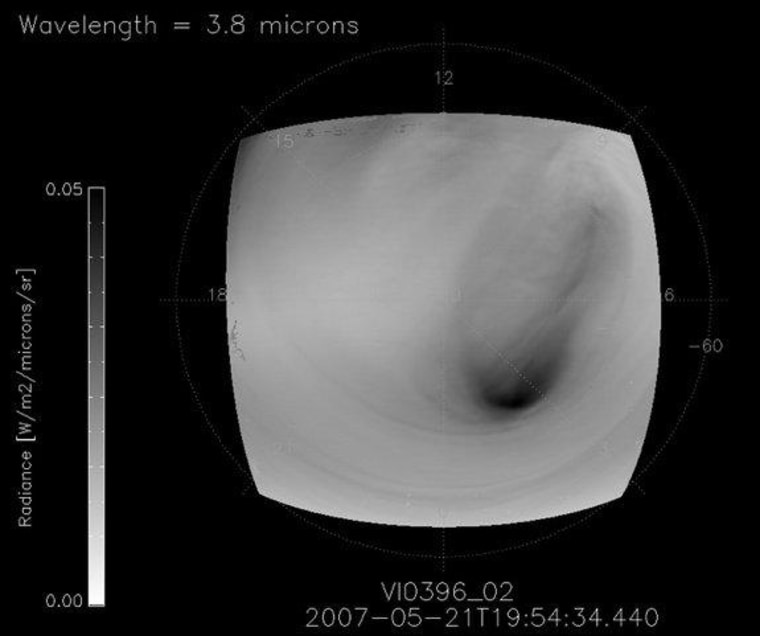
When the European Space Agency's Venus Express satellite arrived at the hot planet in April 2006, it observed a cyclonelike structure above Venus' south pole, four times as large as similar storms on Earth. Over the past six years, the spacecraft has collected daily observations about the storm, which resembles one spotted over Venus' north pole by NASA's Pioneer Venus spacecraft in 1979.
"Both vortices are probably permanent features in the atmosphere of Venus," planetary scientist Itziar Garate-Lopez, of the University of the Basque Country in Spain, told Space.com by email.
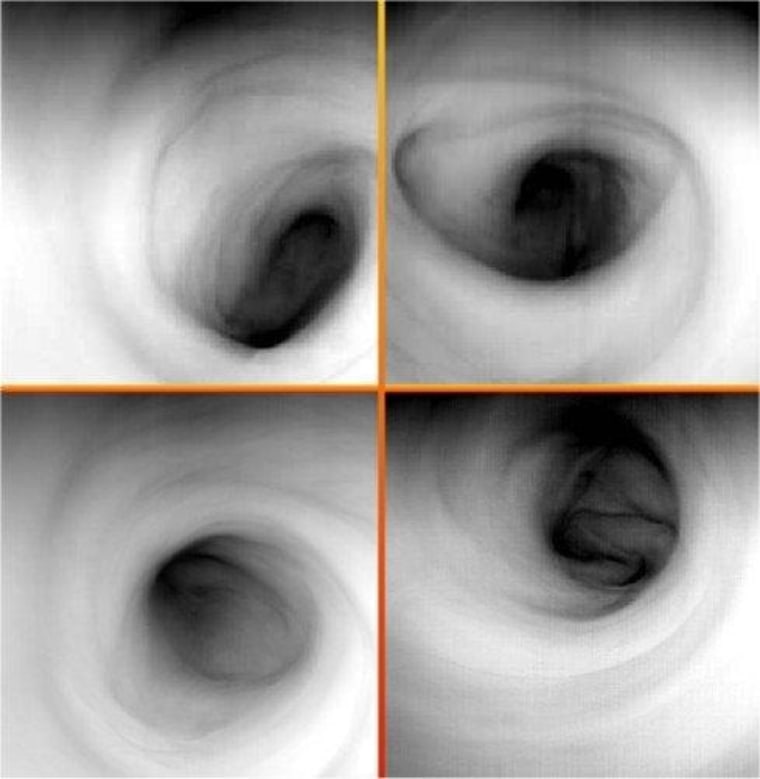
Using the observations taken by Venus Express, Garate-Lopez and her team concluded that the giant storm is in constant flux. Elements of the vortex are constantly breaking apart and reforming as it circles every 2.2 days. [Amazing Venus Photos by ESA's Venus Express]
"The vortex is never destroyed, but it evolves continuously between morphologies" or shapes, Garate-Lopez said.
The cause for the constant evolution remains a puzzle that the team still hopes to solve.
Using the spacecraft's Visible and Infrared Thermal Imaging Spectrometer (VIRTIS), the scientists probed the upper and lower layers of the planet's atmosphere. They concluded that the two centers of rotation of the 12-mile-high (20 kilometers) storm, which exist at different altitudes, rarely line up, a surprising find.
"Even if the small-scale structures are different at both altitude levels, the overall morphology of the vortex is conserved, so we thought that the vortex should move as one large-scale feature in the same way in both vertical layers," Garate-Lopez said. "However, this is not the case."
The constantly shifting centers create what Garate-Lopez calls a "twisted tube" in the vortex.
Although VIRTIS can observe the upper and lower layers of the atmosphere, the middle section remains hidden, keeping the team from more fully understanding the off-kilter movement.
The results were published online Sunday in the journal Nature Geoscience.
A bizarre atmosphere
Venus spins slowly on its axis, taking 243 Earth-days for the sun to rise and set once. But Venus' atmosphere moves significantly faster, circling the planet once every four Earth days.
"The main unsolved question about the atmosphere of Venus is precisely the reason why it super-rotates much faster than the solid planet," Garate-Lopez said.
The relationship between the oddly moving atmosphere and the vortices also remains a mystery.
The cyclone sits 26 miles (42 km) above the surface of the planet. No rain falls from the towering storm, because the planet's atmosphere evaporates all particles within 22 miles (35 km) of the ground. Winds are also inconsequential far beneath the storm.
"If we were at Venus' south pole, we may observe a permanent whirl of clouds high above our heads, with no consequences at the surface," Garate-Lopez said.
Follow Space.com @Spacedotcom, Facebook and Google+. Original article on Space.com.
Copyright 2013 Space.com, a TechMediaNetwork company. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten or redistributed.